What Is What Is The Main Difference Between A Notebook And Ultrabook?

I’ve always been curious about the distinction between a notebook and an ultrabook. After all, both of these portable devices seem very similar, with their compact size, lightweight design, and ability to perform various tasks. However, upon further investigation, I discovered that there is indeed a significant difference between the two. While notebooks are known for their versatility and affordability, ultrabooks are praised for their speed, power, and sleek design. But there’s more to it than meets the eye, so let’s delve deeper into the main disparities between a notebook and ultrabook.
Understanding Notebooks and Ultrabooks
When it comes to choosing a portable computing device, the options can be overwhelming. Among the popular choices are notebooks and ultrabooks, which are often used interchangeably. However, there are key differences between these devices that can greatly affect the user experience. In this article, I will explore the definitions, historical backgrounds, physical design differences, hardware compatibility, portability and battery life, software and performance, pricing differences, market share and user preferences, durability and lifespan, and accessibility and connectivity of notebooks and ultrabooks.
Definition of a notebook
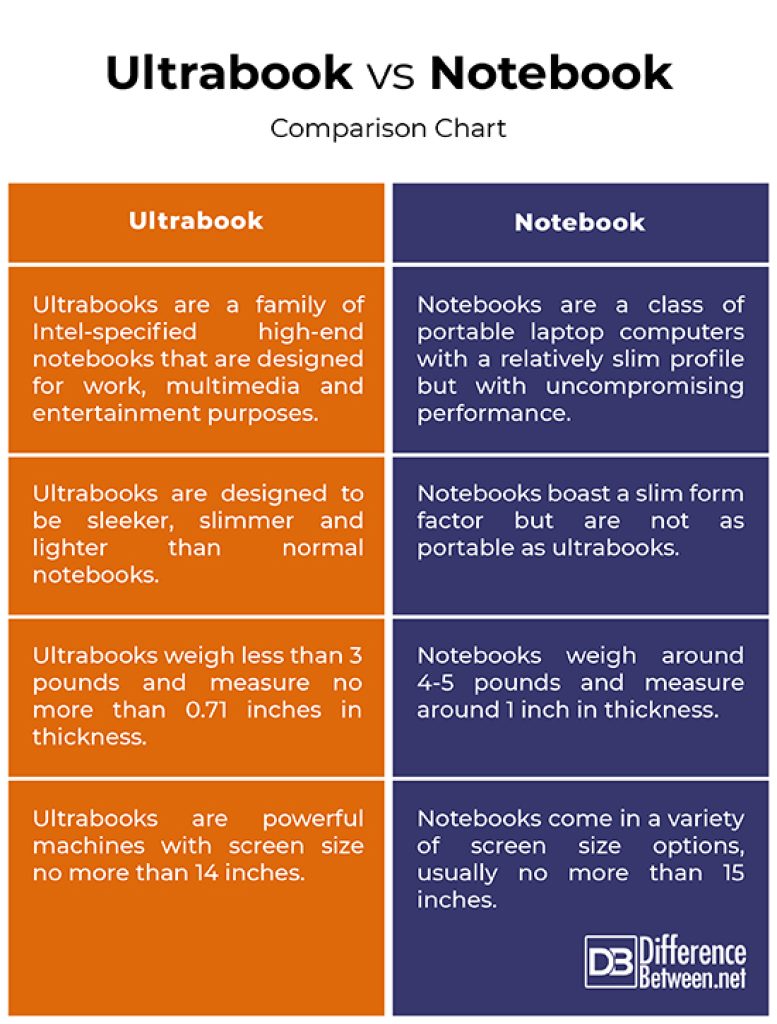
A notebook, also known as a laptop, is a portable personal computer. Its name derives from its ability to be used on one’s lap. Notebooks typically have a clamshell design, with a hinged screen lid that can be opened and closed. They are versatile devices that can perform a wide range of tasks, from basic web browsing and document editing to intensive graphic design and gaming.
This image is property of cdn.differencebetween.net.
Definition of an ultrabook
On the other hand, an ultrabook is a specific type of notebook that meets certain criteria set by Intel, the creator of the Ultrabook brand. An ultrabook is designed to be thin, lightweight, and energy-efficient, without compromising on performance. It combines the portability of a tablet with the functionality of a traditional laptop. Ultrabooks often come with solid-state drives (SSDs) for faster data access and longer battery life.
Historical background of the two terms
The term “notebook” has been in use since the 1990s, as laptops became smaller and more portable compared to their desktop counterparts. However, the term “ultrabook” is relatively new, coined by Intel in 2011 to describe a new category of ultraportable laptops. Intel aimed to compete with the rising popularity of tablets by creating a new standard for slim and lightweight laptops. Since then, ultrabooks have gained recognition in the market and have become a popular choice for users seeking both portability and power.

This image is property of www.ultrabookreview.com.
Physical Design Differences
One of the most noticeable differences between notebooks and ultrabooks is their physical design. Ultrabooks are known for their slim and sleek appearance, while notebooks tend to be bulkier. This difference in size and weight can greatly impact portability and user experience.
Size and weight comparison
Ultrabooks are designed to be ultra-thin and lightweight. They typically have a thickness of less than 0.7 inches and weigh around 2-3 pounds. This slim design makes them easy to carry around, fitting into a backpack or briefcase without weighing you down. In comparison, notebooks can vary in size and weight depending on their specifications. While some notebooks can be similar in size and weight to ultrabooks, there are also larger and heavier models available.
Screen size and resolution
In terms of screen size and resolution, notebooks and ultrabooks offer a range of options to suit different user preferences. Ultrabooks often prioritize portability, so they commonly feature screens between 12 to 14 inches. This size strikes a balance between a compact form factor and a comfortable viewing experience. Notebooks, on the other hand, are available in various sizes, ranging from 11 to 17 inches or more. This allows users to choose a larger screen size for tasks that require more screen real estate.
Keyboard and touchpad design differences
Another aspect where notebooks and ultrabooks differ is the design of their keyboards and touchpads. Ultrabooks typically have shallow keyboards with low travel distance, similar to those found on tablets or smartphones. While this design choice helps maintain a slim profile, it may not be as comfortable for users who prefer a tactile typing experience. Notebooks, on the other hand, often feature keyboards with greater key travel, which can enhance typing comfort, especially for long typing sessions. Touchpad designs may also vary, with ultrabooks often having smaller touchpads due to space constraints.
Hardware Compatibility
When comparing notebooks and ultrabooks, it’s essential to consider the hardware differences that can affect their performance and usability.
Processor differences
Both notebooks and ultrabooks are equipped with powerful processors. However, ultrabooks often feature the latest generation of energy-efficient processors, such as Intel’s Core i5 or Core i7 processors. These processors offer a good balance between performance and power consumption, allowing ultrabooks to deliver solid performance while maintaining long battery life. Notebooks, on the other hand, may come with a wider range of processor options, including high-performance processors for demanding tasks.
RAM and storage options
In terms of RAM and storage options, both notebooks and ultrabooks have similar capabilities. They can be equipped with varying amounts of RAM, typically ranging from 4GB to 16GB or more. This allows users to choose a configuration that suits their multitasking needs. Similarly, both devices offer a range of storage options, including traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) and faster solid-state drives (SSDs). Ultrabooks often prioritize SSDs for their faster read and write speeds, contributing to faster boot times and overall responsiveness.
Graphics performance and capabilities
Graphics performance is another important consideration, especially for users who need their devices for gaming, graphic design, or video editing. Ultrabooks typically feature integrated graphics processors, which are sufficient for casual gaming and multimedia consumption. However, notebooks often offer a wider range of graphics options, including dedicated graphics cards from manufacturers like NVIDIA or AMD. These dedicated graphics cards provide enhanced performance and can handle more demanding tasks without compromising on battery life.

This image is property of technewsdaily.com.
Portability and Battery life
Portability and battery life are crucial factors for users who frequently travel or work on the go. Let’s explore how notebooks and ultrabooks compare in terms of portability and battery life.
Battery size and power efficiency
Ultrabooks are designed with energy efficiency in mind, allowing them to deliver longer battery life compared to traditional notebooks. They often feature smaller battery sizes due to their slim form factor, but they balance this by having power-efficient components and optimized software. Notebooks, on the other hand, can come with larger battery sizes but may consume more power due to their higher-power processors and graphics cards.
Comparison of portability
Due to their slim and lightweight design, ultrabooks are generally considered more portable than notebooks. Their compact size allows them to easily fit into smaller bags or backpacks, making them ideal for users constantly on the move. Notebooks, while not as compact, can still be portable depending on their size and weight. Users who prioritize portability may find ultrabooks more suitable, while those who value screen real estate or performance may opt for a larger notebook.
Charging options and power usage
When it comes to charging options and power usage, both notebooks and ultrabooks generally come with similar capabilities. They can be charged through a power adapter connected to a wall socket or through a USB-C port that supports power delivery. Some ultrabooks also offer fast charging options, allowing users to quickly recharge their devices. Power usage can vary depending on the device’s specifications and usage patterns, but both notebooks and ultrabooks are designed to be energy-efficient to maximize battery life.
Software and Performance
The software and performance aspects of notebooks and ultrabooks play a significant role in the user experience. Let’s explore the key differences in operating systems, benchmarking performance, and software compatibility.
Operating systems used
Both notebooks and ultrabooks offer a wide range of operating system choices, with the most common options being Windows, macOS, and Chrome OS. Windows is the most popular operating system, providing broad software compatibility and extensive hardware support. macOS, exclusive to Apple devices, offers a seamless integration with other Apple products and a robust ecosystem of applications. Chrome OS, found primarily on Chromebooks, focuses on web-based applications and cloud computing. Each operating system has its strengths and considerations, so choosing the right one depends on individual needs and preferences.
Benchmarking performance results
Although both notebooks and ultrabooks can deliver excellent performance, there may be slight differences due to the varying specifications and design priorities. Benchmarking tests can provide insights into the specific performance characteristics of each device. Ultrabooks, with their focus on energy efficiency, may demonstrate slightly lower benchmark scores in intense tasks compared to notebooks with high-performance components. However, in day-to-day usage scenarios, the performance gap may not be easily noticeable.
Software compatibility
Software compatibility is an important factor to consider when choosing between a notebook and an ultrabook. While both devices can generally run the same software, there may be some exceptions. Ultrabooks, with their slim form factor, may have limited internal storage space, which can restrict the installation of large software programs or games. Additionally, some specialized software may have specific hardware requirements that notebooks, with their wider range of configuration options, can better accommodate.

This image is property of cdn.differencebetween.net.
Pricing Differences
Price is often a significant consideration when making a purchasing decision. Let’s delve into the pricing differences between notebooks and ultrabooks.
Price range of notebooks
Notebooks come in a wide range of price points, making them accessible to a broader audience. Entry-level models can start at around $300 and go up to several thousand dollars for high-end gaming or professional-use laptops. The price variation is due to factors such as brand reputation, specifications, build quality, and additional features.
Price range of ultrabooks
Ultrabooks, being a premium category of laptops, tend to have a higher price range compared to standard notebooks. They often start at around $800 and can exceed $2000 or more for top-of-the-line models. The higher price reflects the advanced design, energy efficiency, premium materials, and cutting-edge technology used in ultrabooks.
Value for money comparison
When assessing value for money, it’s important to consider the intended use and budget constraints. While ultrabooks generally command a higher price, they offer better portability, sleeker designs, longer battery life, and optimized performance. Notebooks, on the other hand, provide a wider range of configurations and price points, making them suitable for a broader audience with varying needs and budgets. Ultimately, choosing between a notebook and an ultrabook depends on individual priorities and financial constraints.
Market Share and User Preference
To gain a better understanding of the popularity and user preferences between notebooks and ultrabooks, let’s explore the current market share and user reviews.
Current market share of notebooks and ultrabooks
Notebooks, being the traditional form of portable computers, have a more significant market share compared to ultrabooks. Their longstanding presence and versatility have made them a go-to choice for many users. However, ultrabooks have gained rapid traction in recent years due to their sleek design, high portability, and impressive performance. They have carved a niche market for users who prioritize enhanced mobility without sacrificing productivity.
User reviews and preferences
User reviews and preferences can provide valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of both notebooks and ultrabooks. Notebooks are appreciated for their versatility, wide range of configuration options, and affordability. Users often praise their ability to handle demanding tasks and their flexibility for both personal and professional use. Ultrabooks, on the other hand, are lauded for their slim and lightweight designs, long battery life, and overall user experience. Users frequently commend their portability and performance, especially for on-the-go productivity or entertainment.
Target audience for both devices
While both notebooks and ultrabooks cater to a wide range of users, there are specific target audiences for each device. Notebooks, with their versatility and flexible price points, appeal to a broad spectrum of users including students, professionals, gamers, and casual users. Ultrabooks, with their emphasis on portability and premium design, are often favored by frequent travelers, business professionals, content creators, and individuals who prioritize style and convenience in their computing devices.

This image is property of steemitimages.com.
Durability and Lifespan
Durability and lifespan are important considerations when investing in a portable computing device. Let’s evaluate the build quality and longevity of notebooks and ultrabooks.
Build quality comparison
Ultrabooks are known for their premium build quality, often featuring lightweight yet sturdy materials such as aluminum or carbon fiber. The attention to detail in their design and construction contributes to their durability and resistance to everyday wear and tear. Notebooks, with their wider range of options, can vary in build quality depending on the manufacturer and price point. High-end notebooks often incorporate robust materials and precision engineering, while budget-friendly options may sacrifice some durability to achieve lower costs.
Lifespan and longevity of both devices
Both notebooks and ultrabooks are designed to last for several years with proper care and maintenance. The lifespan of a device depends on factors such as usage patterns, software updates, storage conditions, and overall build quality. With regular software updates and hardware maintenance, it is not uncommon for a well-maintained notebook or ultrabook to last for at least 5-7 years or more.
Repair and maintenance aspects
When it comes to repair and maintenance, notebooks generally offer more options due to their wider availability and popularity. Various service centers and third-party repair shops specialize in notebook repairs, making it relatively easy to find spare parts and professional assistance. Ultrabooks, while also repairable, may have more limited options depending on the specific model and availability of spare parts. It’s worth considering the repair and maintenance aspects when choosing between a notebook and an ultrabook.
Accessibility and Connectivity
The accessibility and connectivity features of notebooks and ultrabooks significantly impact their usability and versatility. Let’s delve into the available ports, wireless capabilities, and external accessories compatibility.
Available ports and connectivity options
Notebooks and ultrabooks offer a range of ports and connectivity options to connect to various devices and peripherals. Common ports found on both devices include USB-A, USB-C, HDMI, and audio jacks. Ultrabooks often prioritize the use of USB-C ports due to their slim design and versatility. Notebooks may offer a wider variety of ports, including older legacy ports like VGA or Ethernet, which can be useful in certain scenarios. The availability of ports and connectivity options depends on the specific model and manufacturer.
Wireless capabilities
Both notebooks and ultrabooks come with built-in wireless capabilities, including Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. These wireless technologies enable users to connect to the internet, transfer files, and pair with wireless peripherals such as mice, keyboards, and speakers. Ultrabooks generally offer the latest Wi-Fi standards, such as Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax), which can provide faster and more stable wireless connections. Notebooks may also support Wi-Fi 6, but older models may be limited to earlier Wi-Fi standards.
External accessories compatibility
Being able to connect and use external accessories can greatly enhance the functionality and versatility of notebooks and ultrabooks. Both devices typically support common accessories such as external monitors, printers, scanners, and storage devices. Compatibility can vary depending on the operating system and the specific hardware requirements of the accessory. It’s advisable to check the compatibility and system requirements of external accessories before making a purchase.
Conclusion on the Main Difference
In conclusion, notebooks and ultrabooks have distinct differences that make them suitable for different users and use cases. Notebooks offer a wider range of options in terms of size, specifications, and price points. They are versatile workhorses that can handle a variety of tasks, making them a popular choice for both casual and professional users. Ultrabooks, on the other hand, prioritize portability, sleek design, and energy efficiency. They excel in providing a premium user experience, longer battery life, and enhanced mobility. Ultimately, the choice between a notebook and an ultrabook depends on individual preferences, budget, and specific computing needs.







